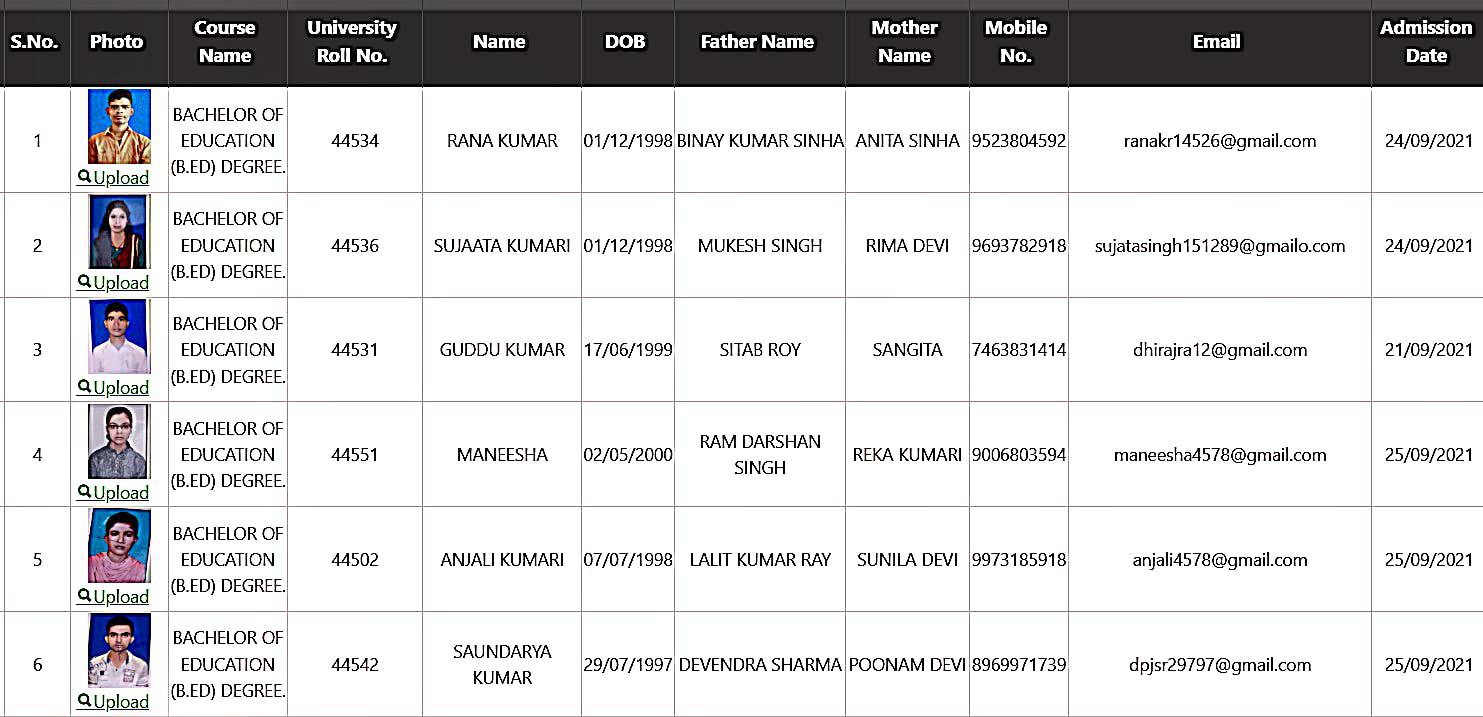
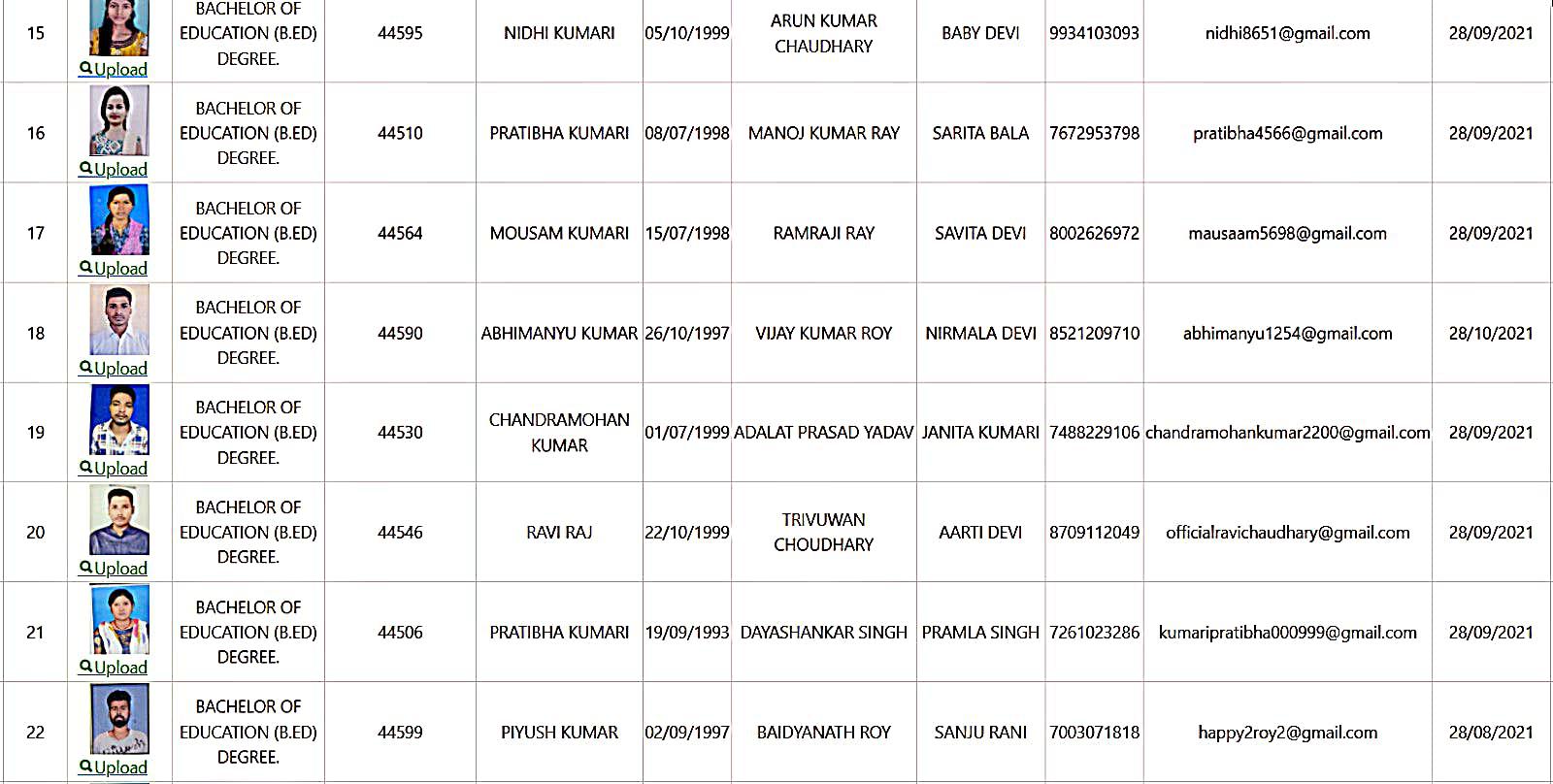
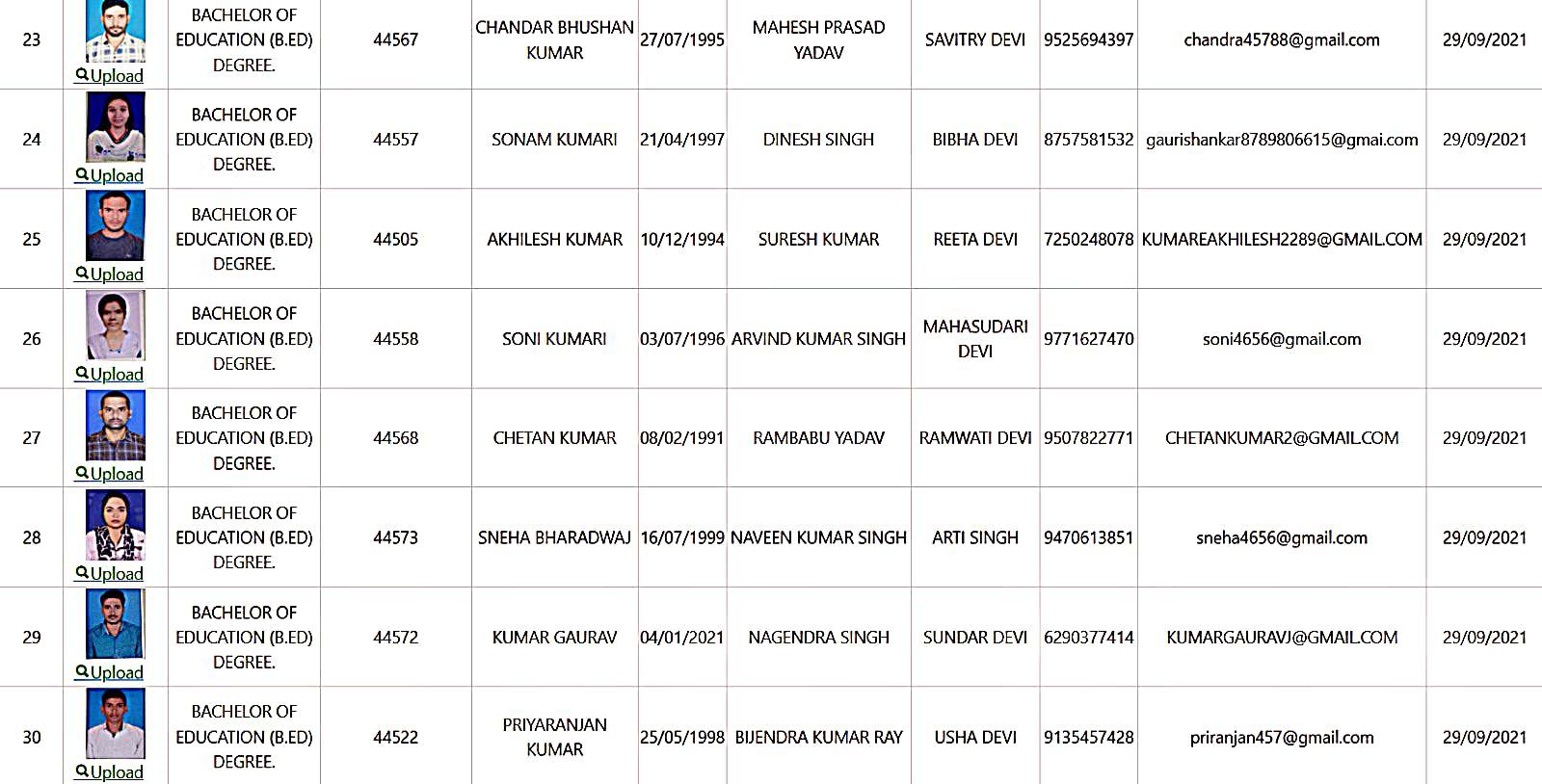
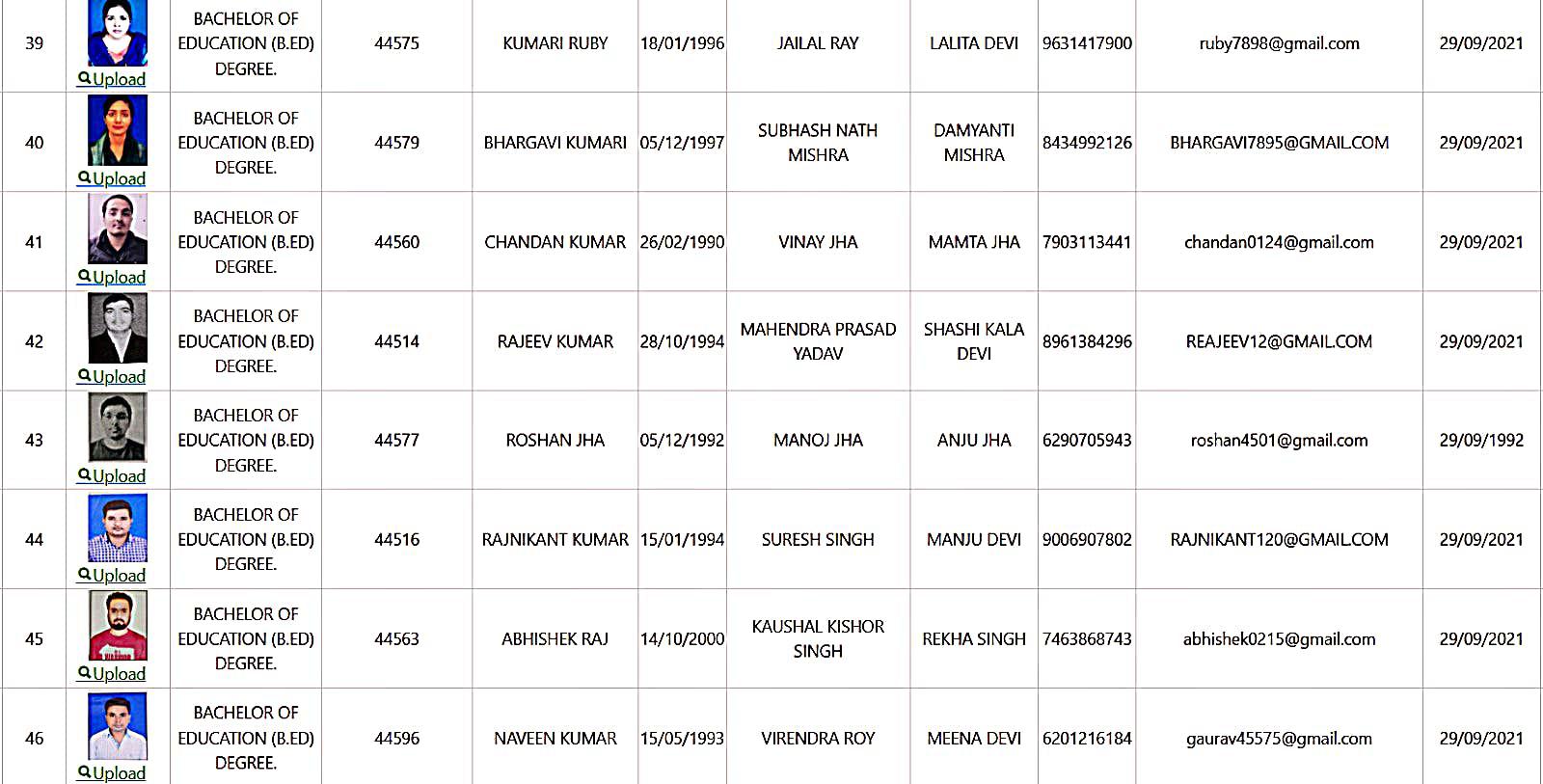
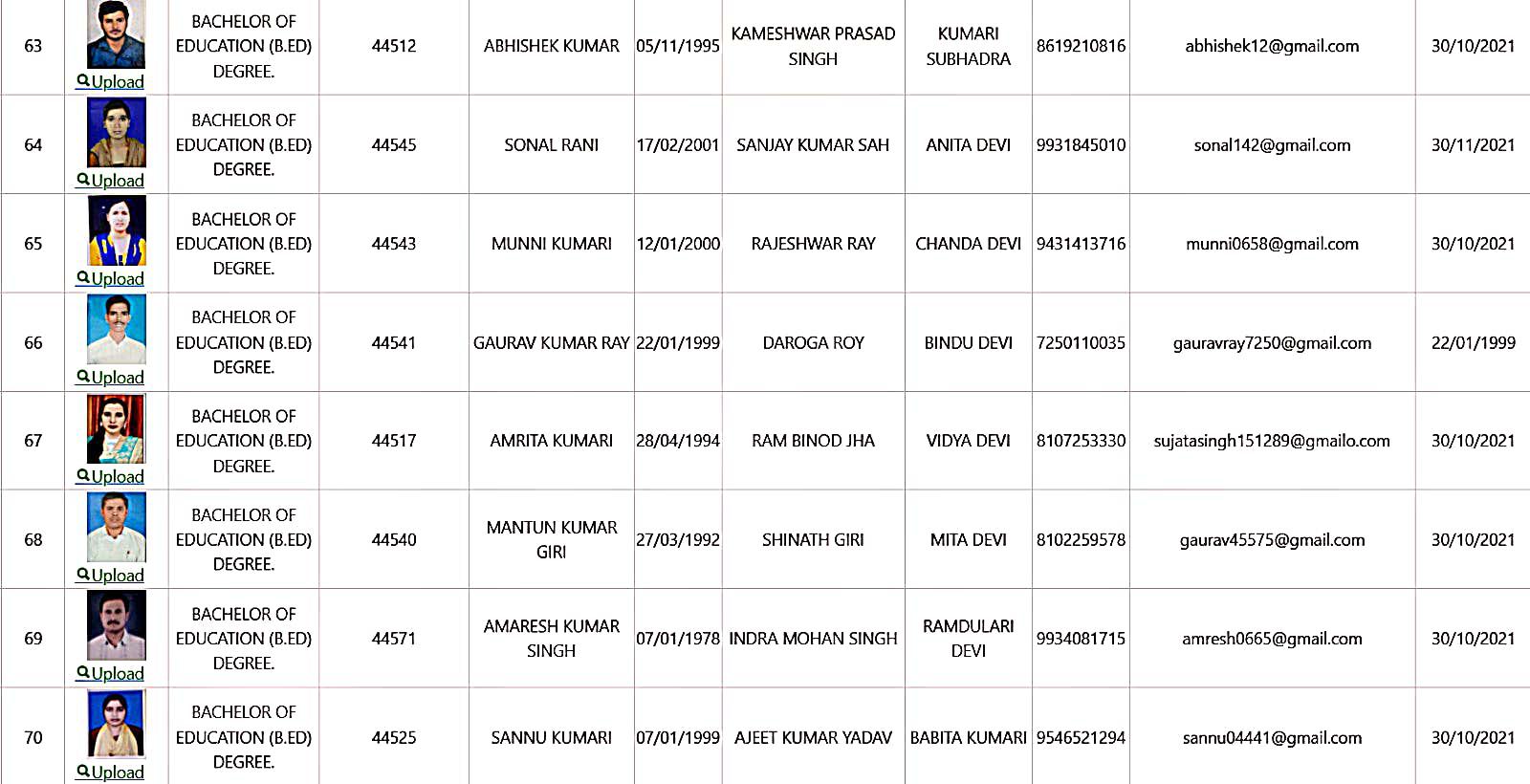
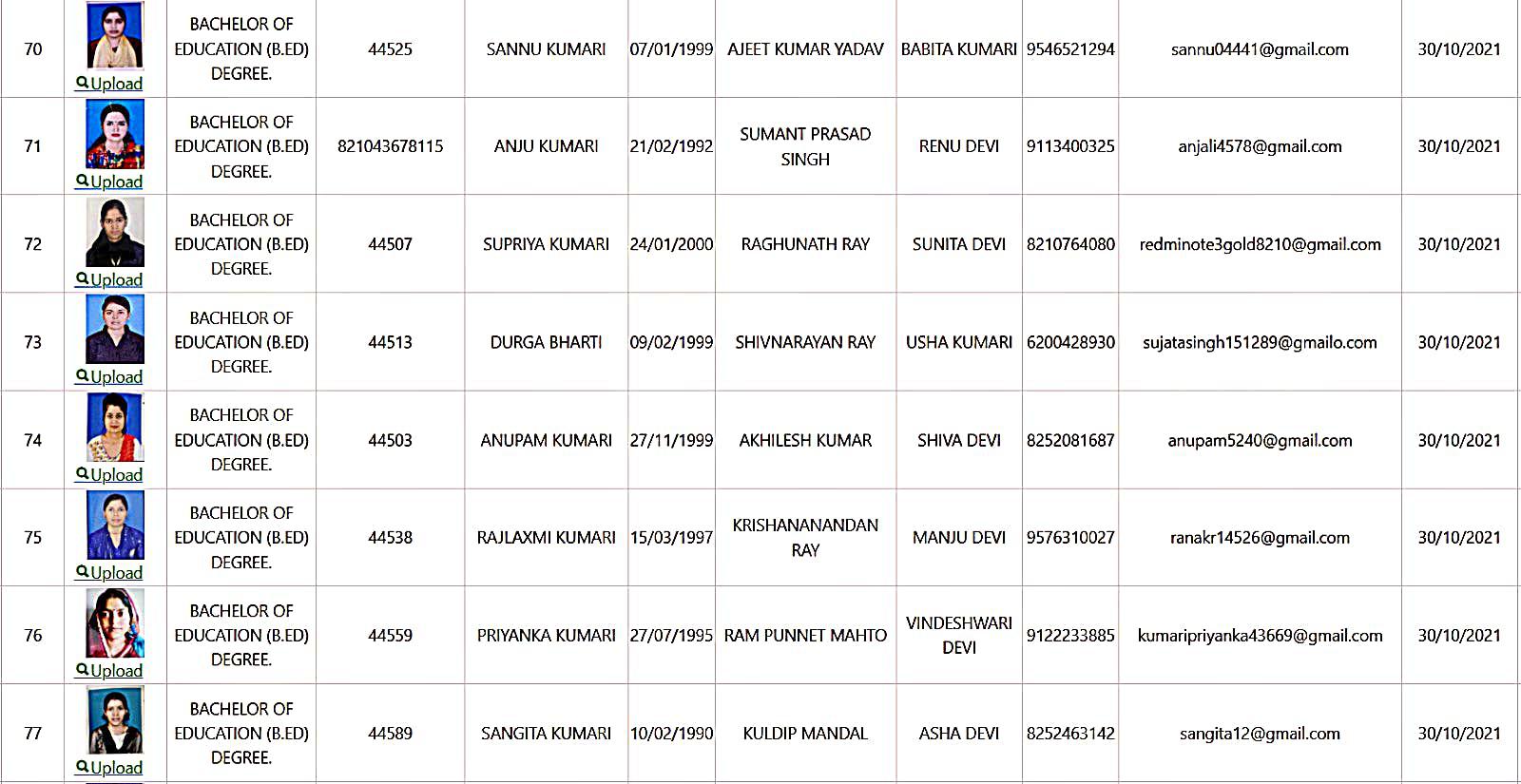
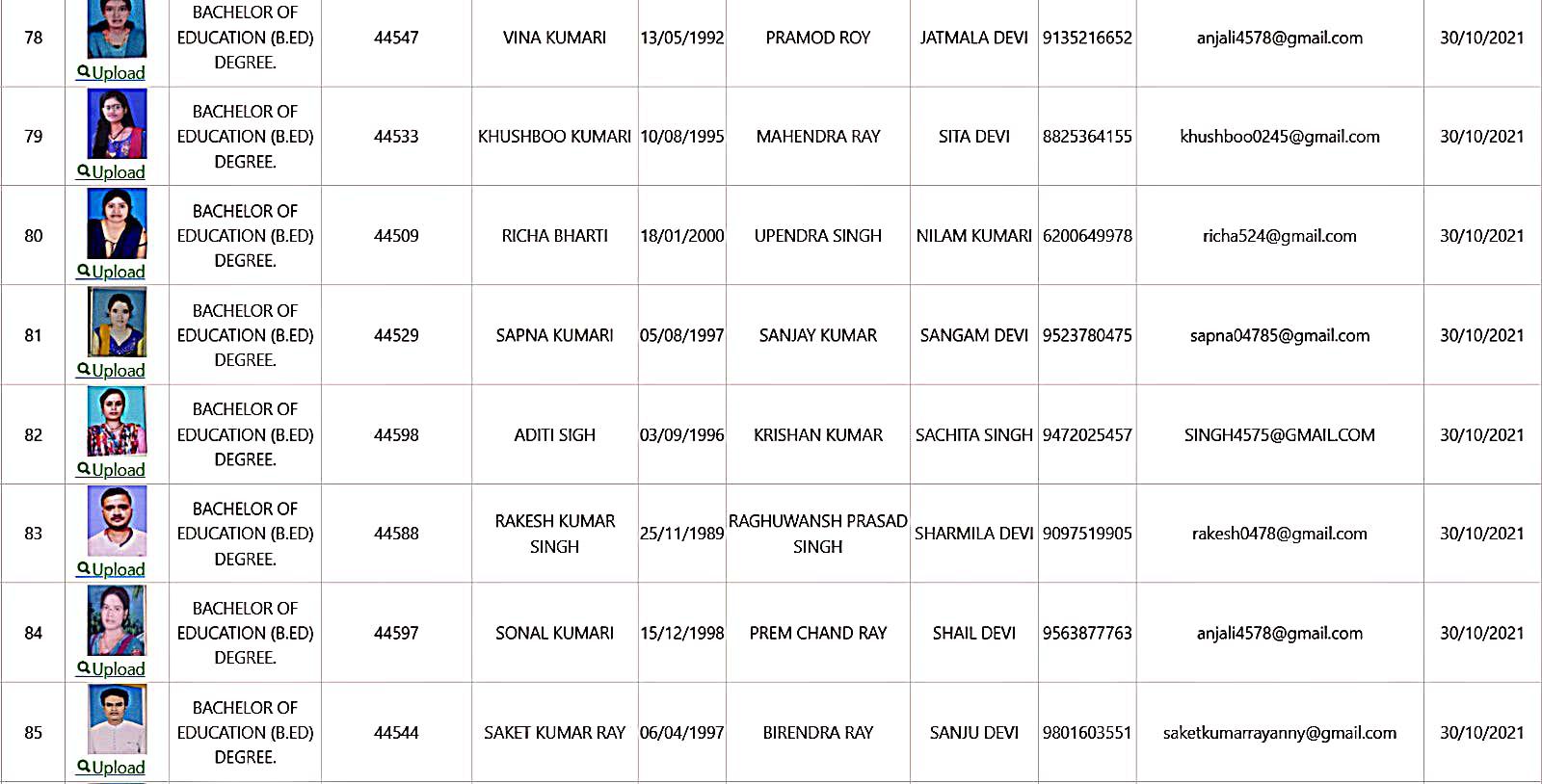
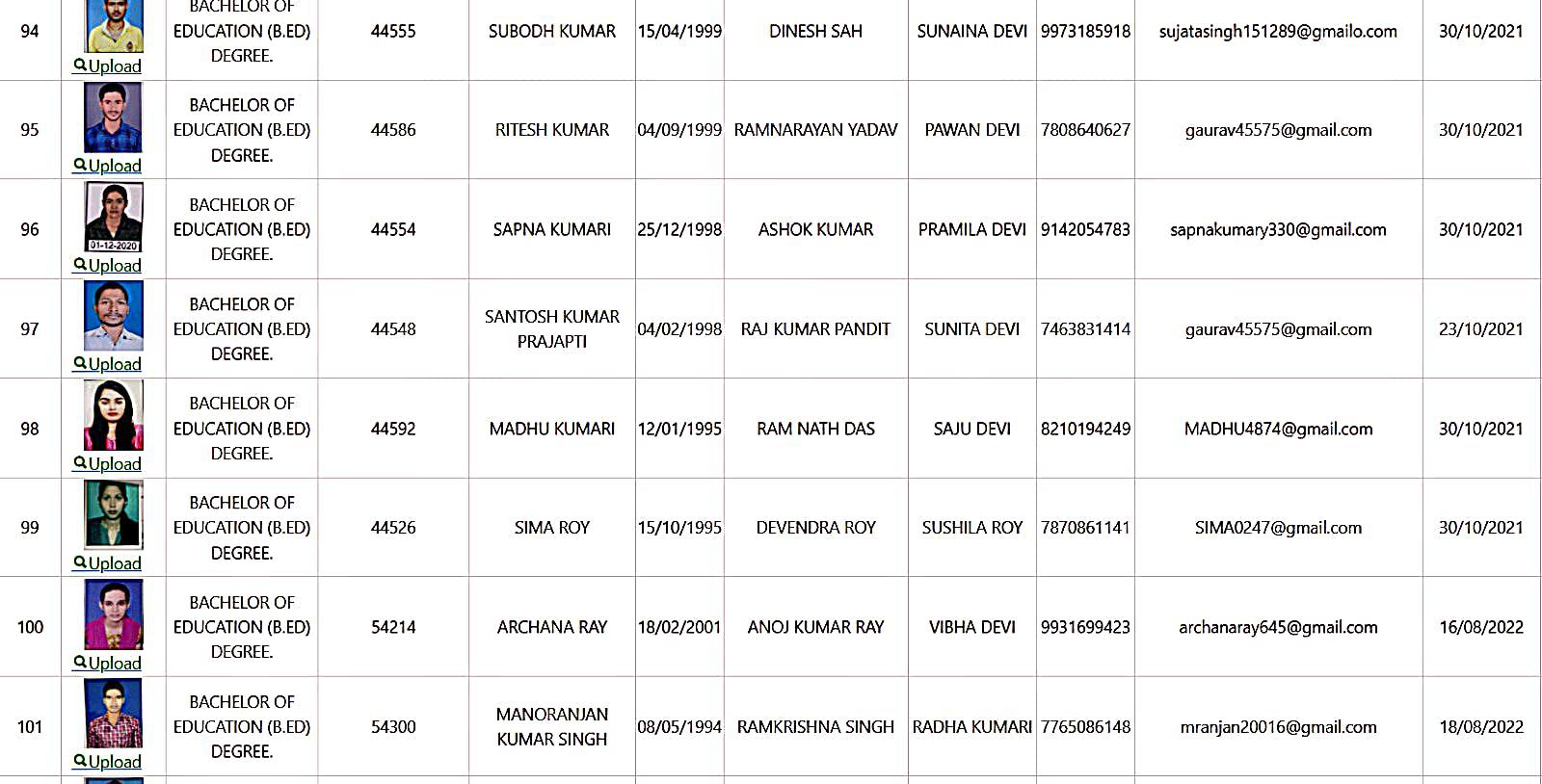
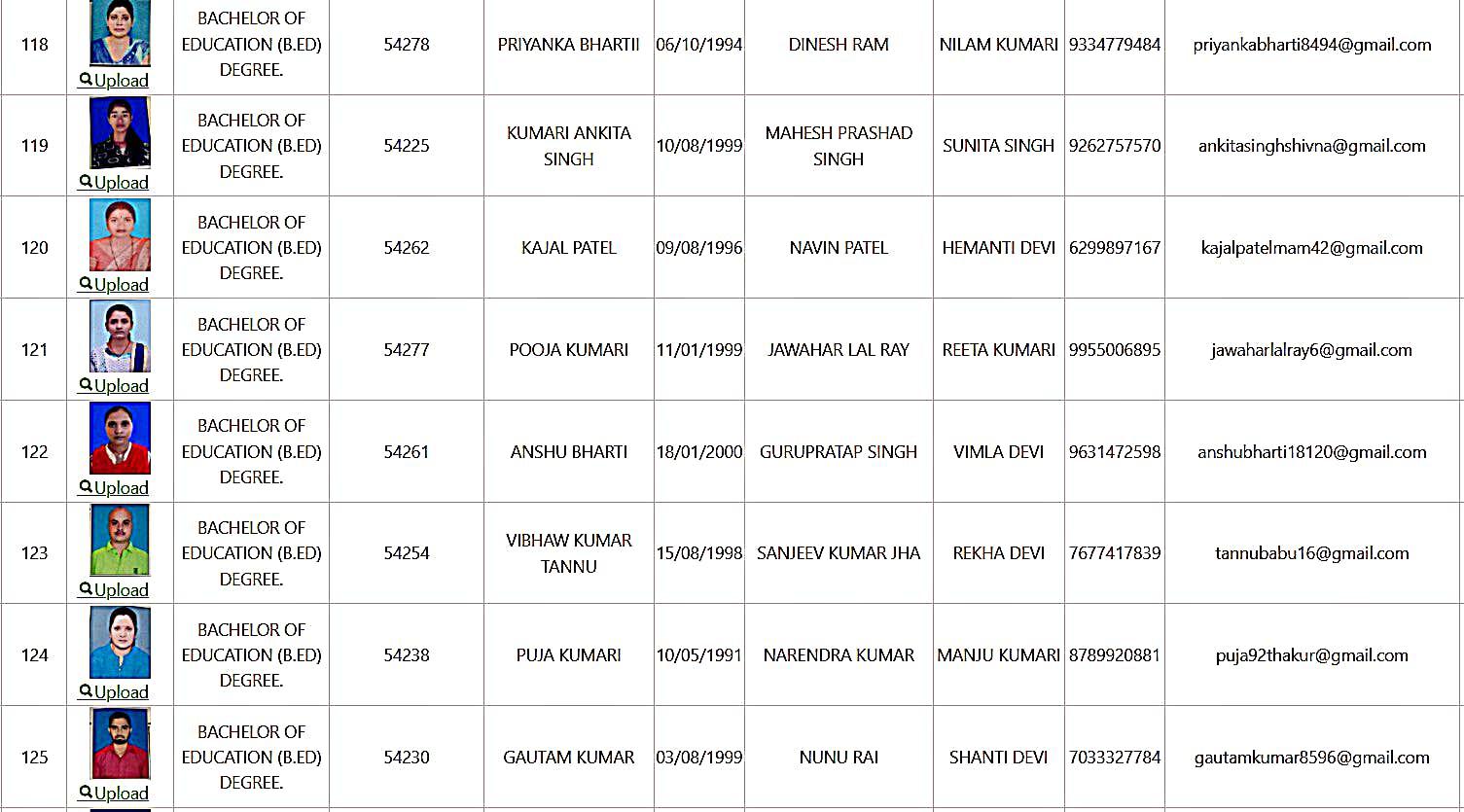
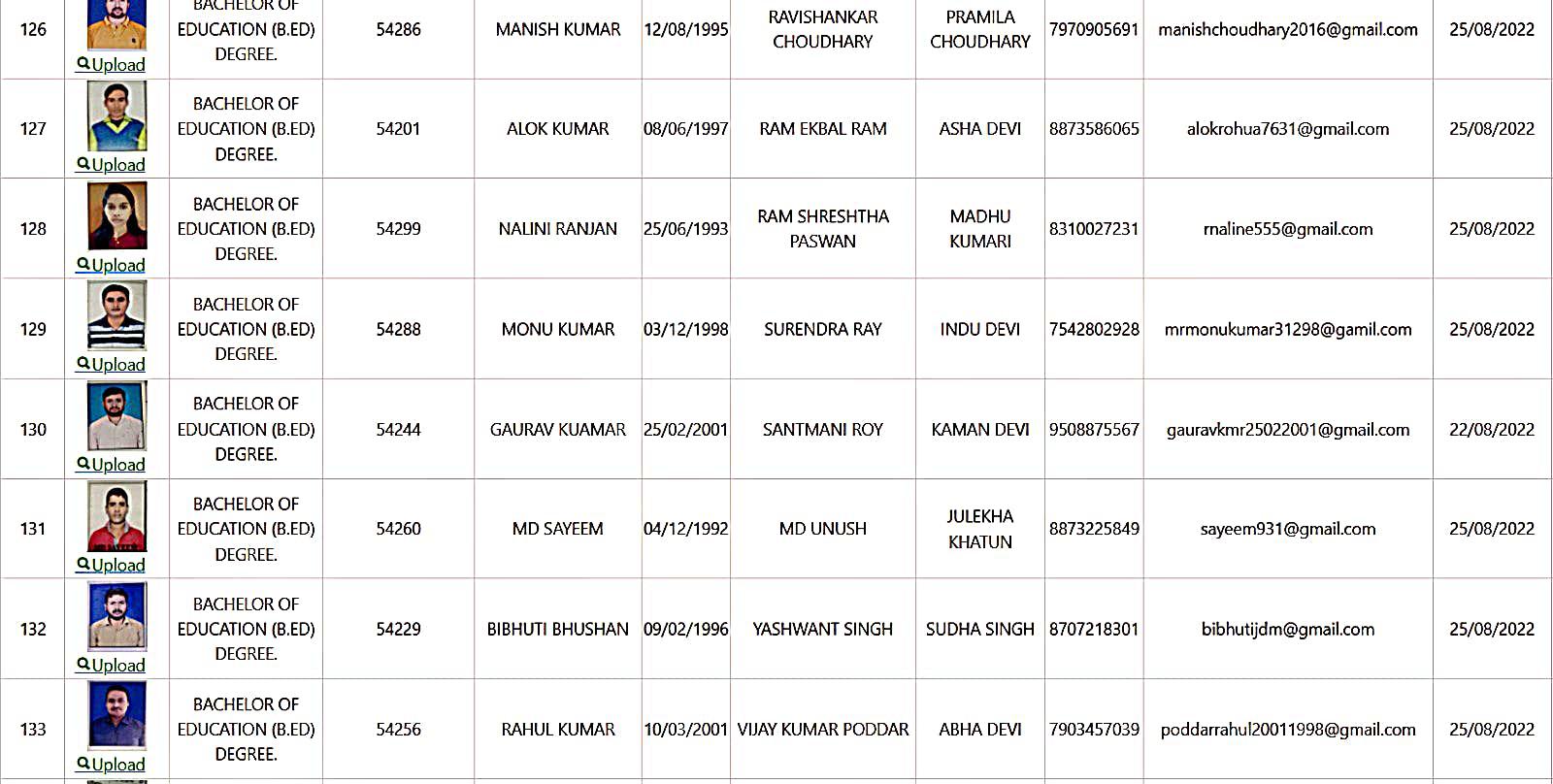
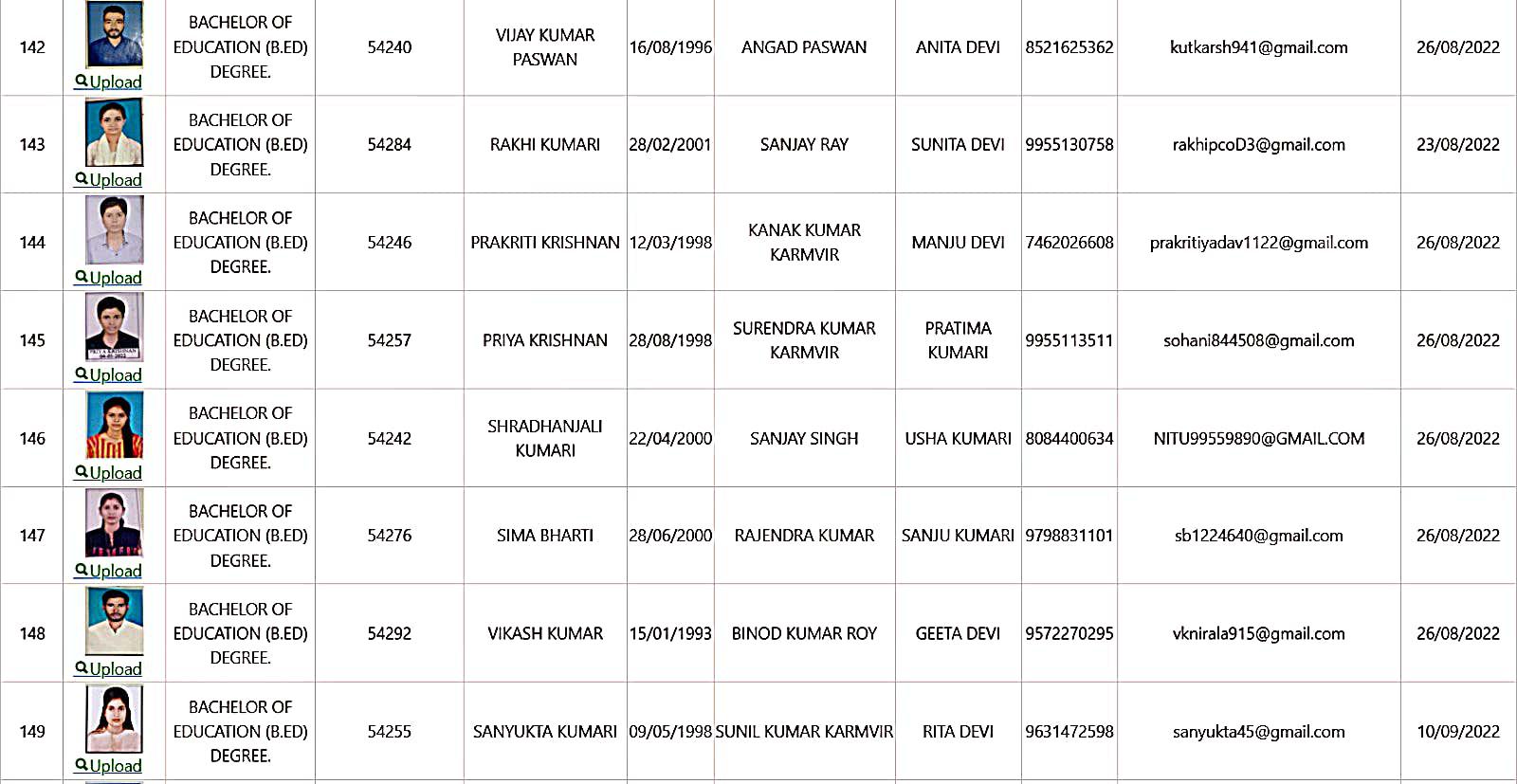
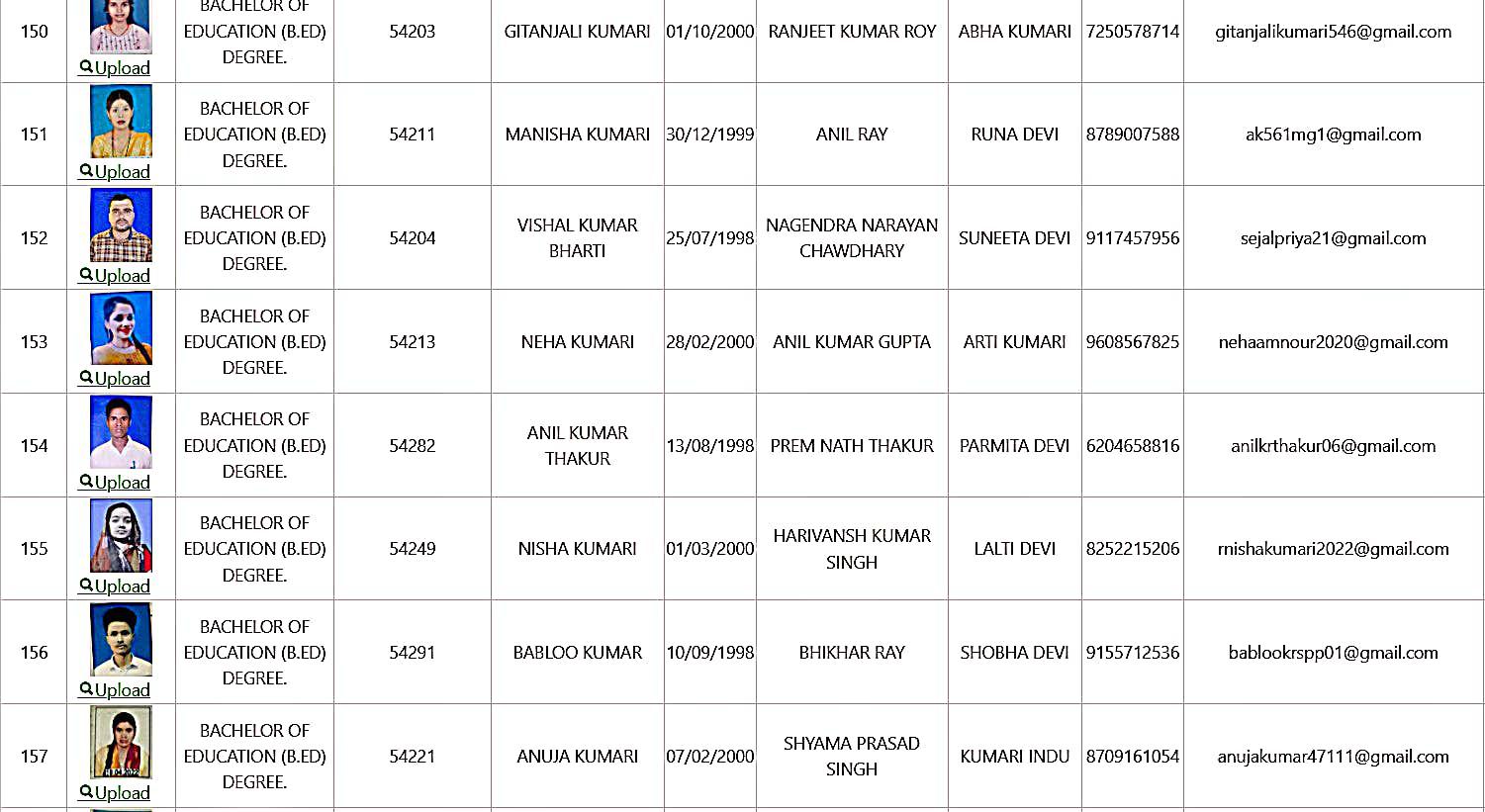
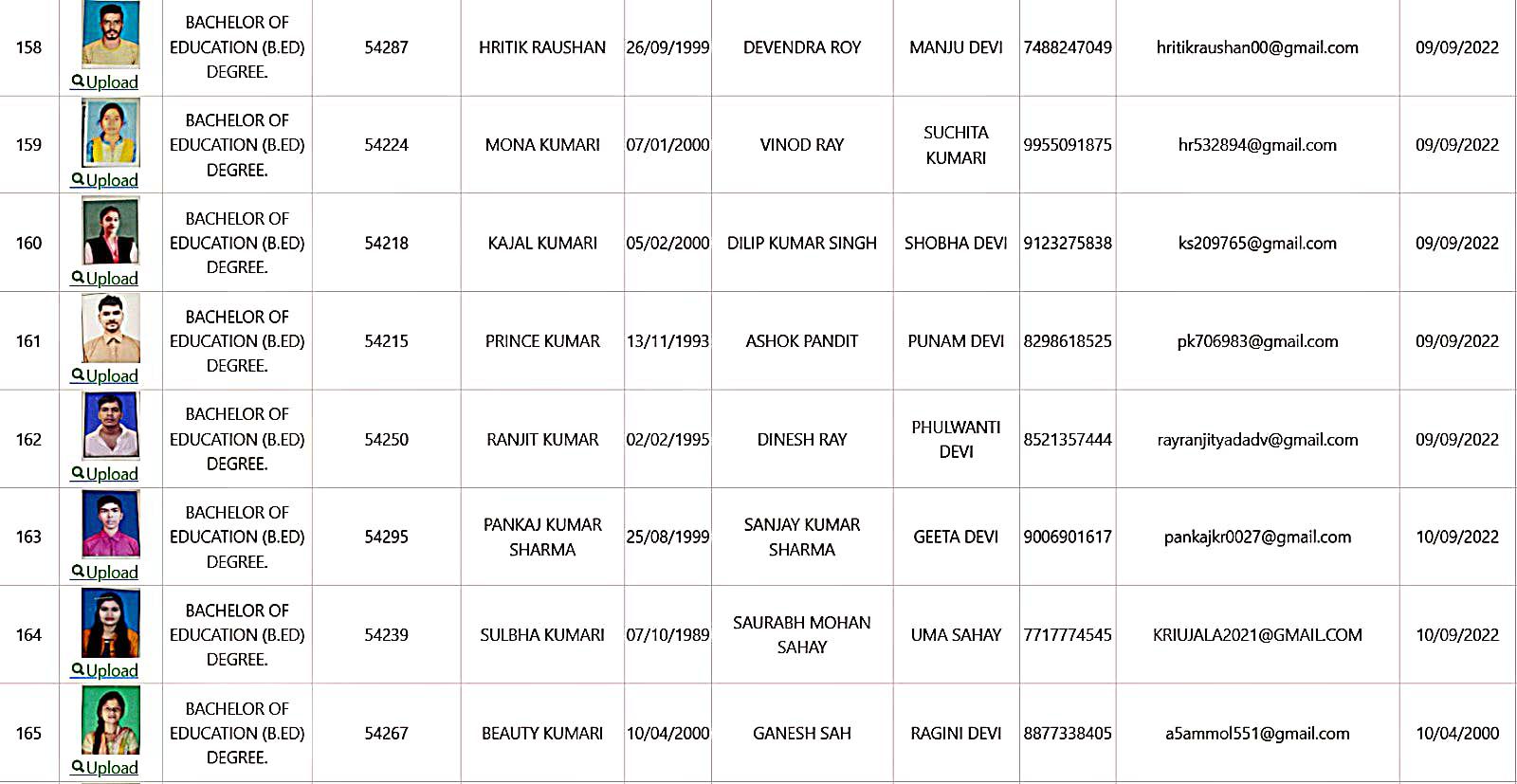
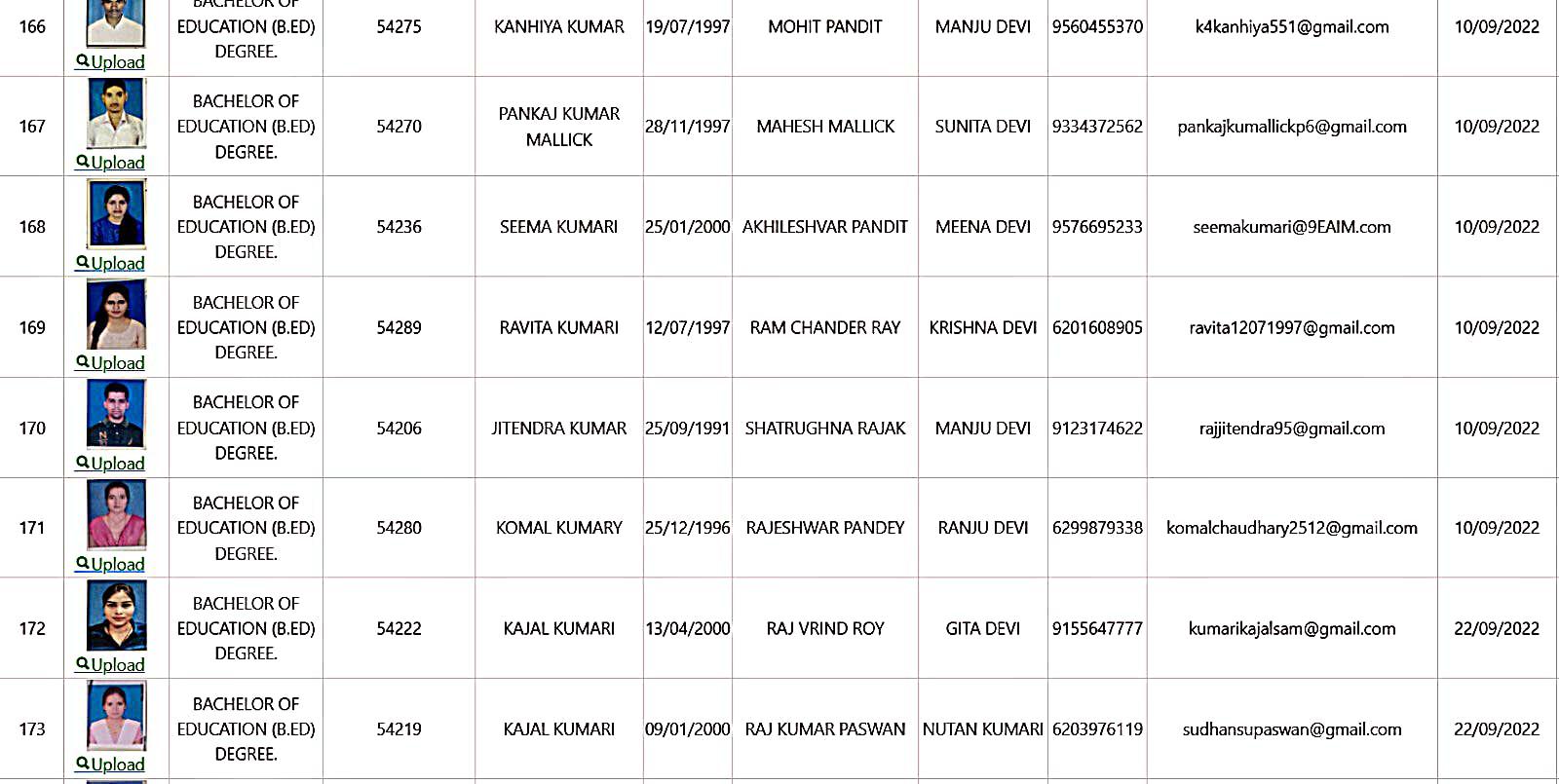
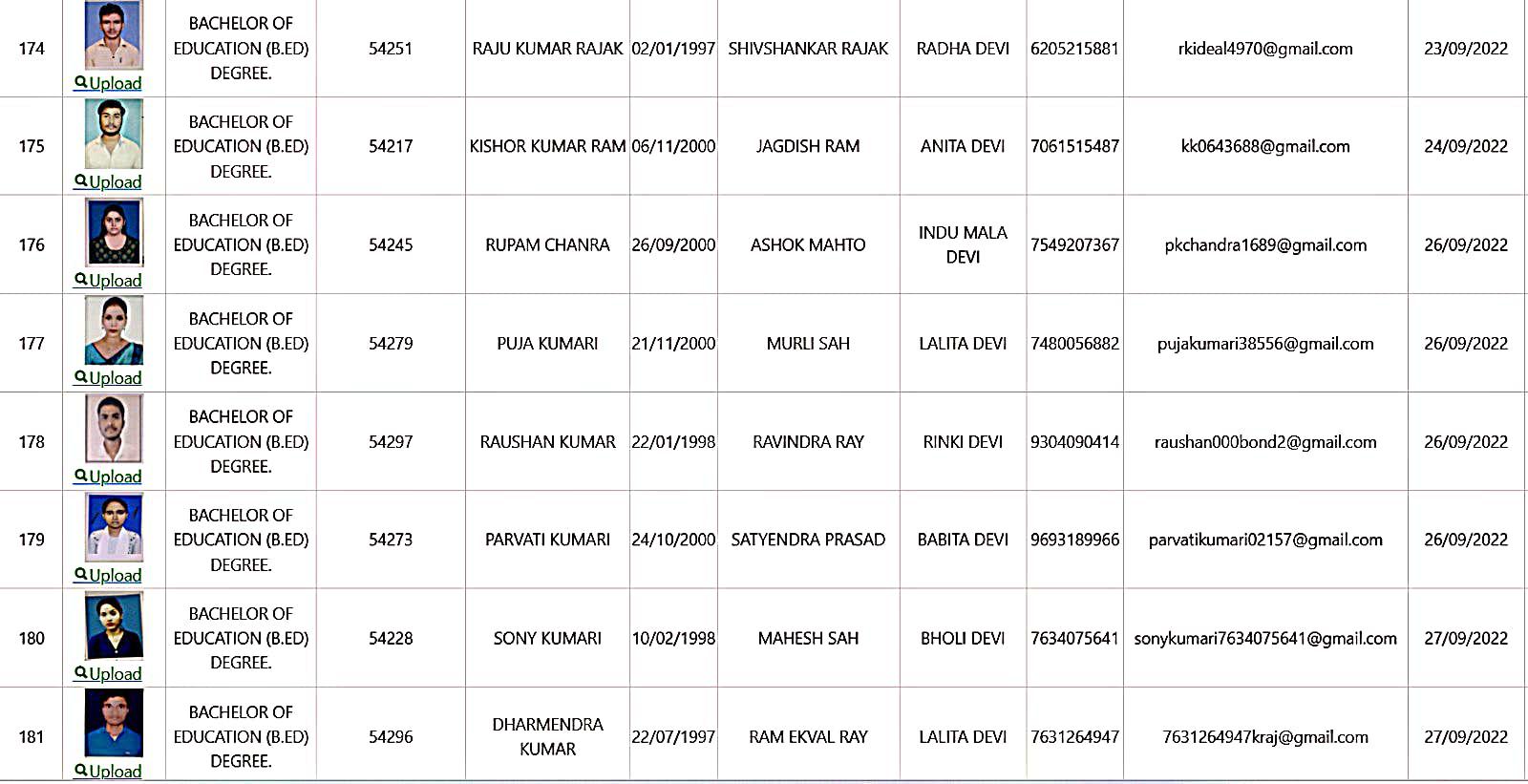
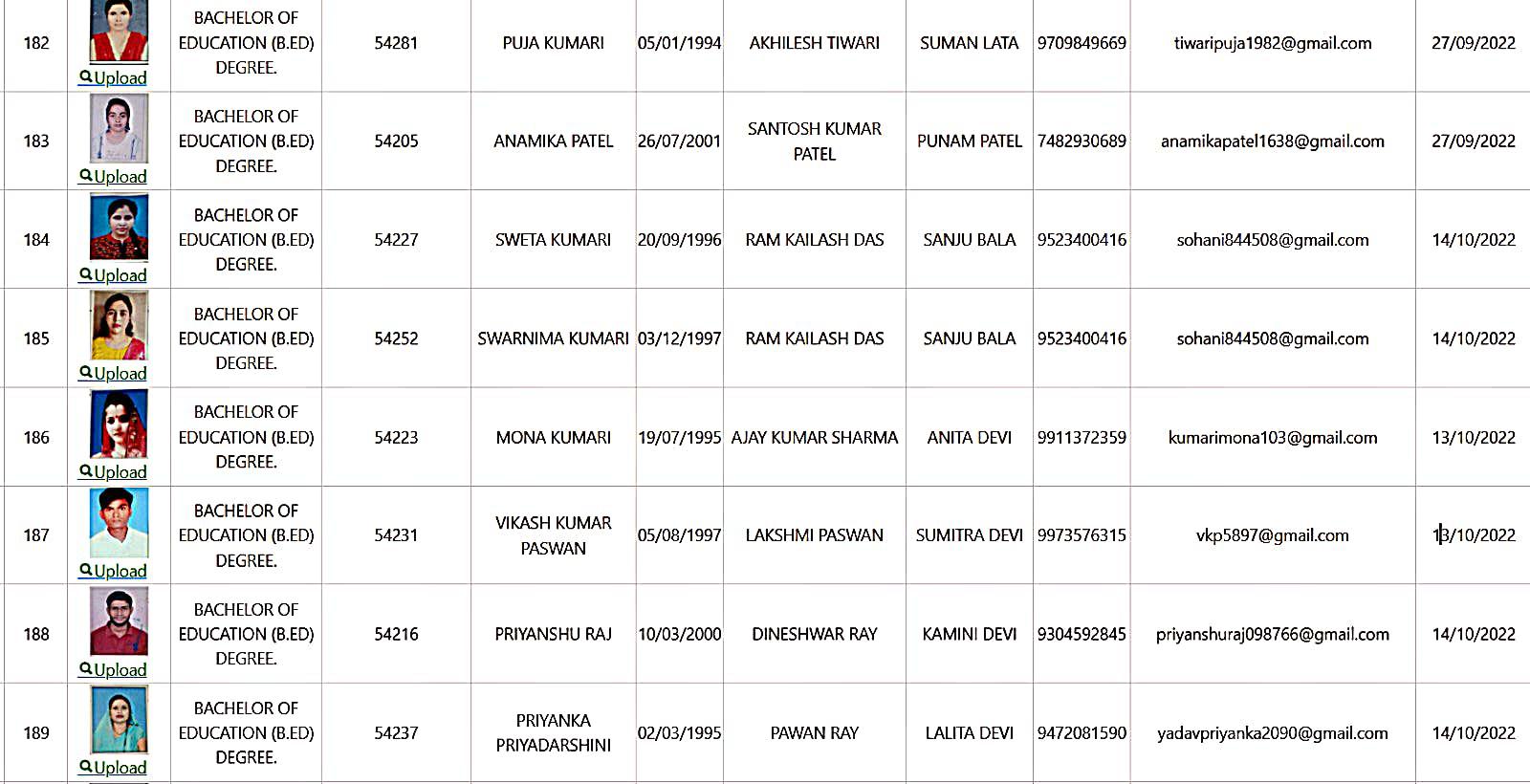
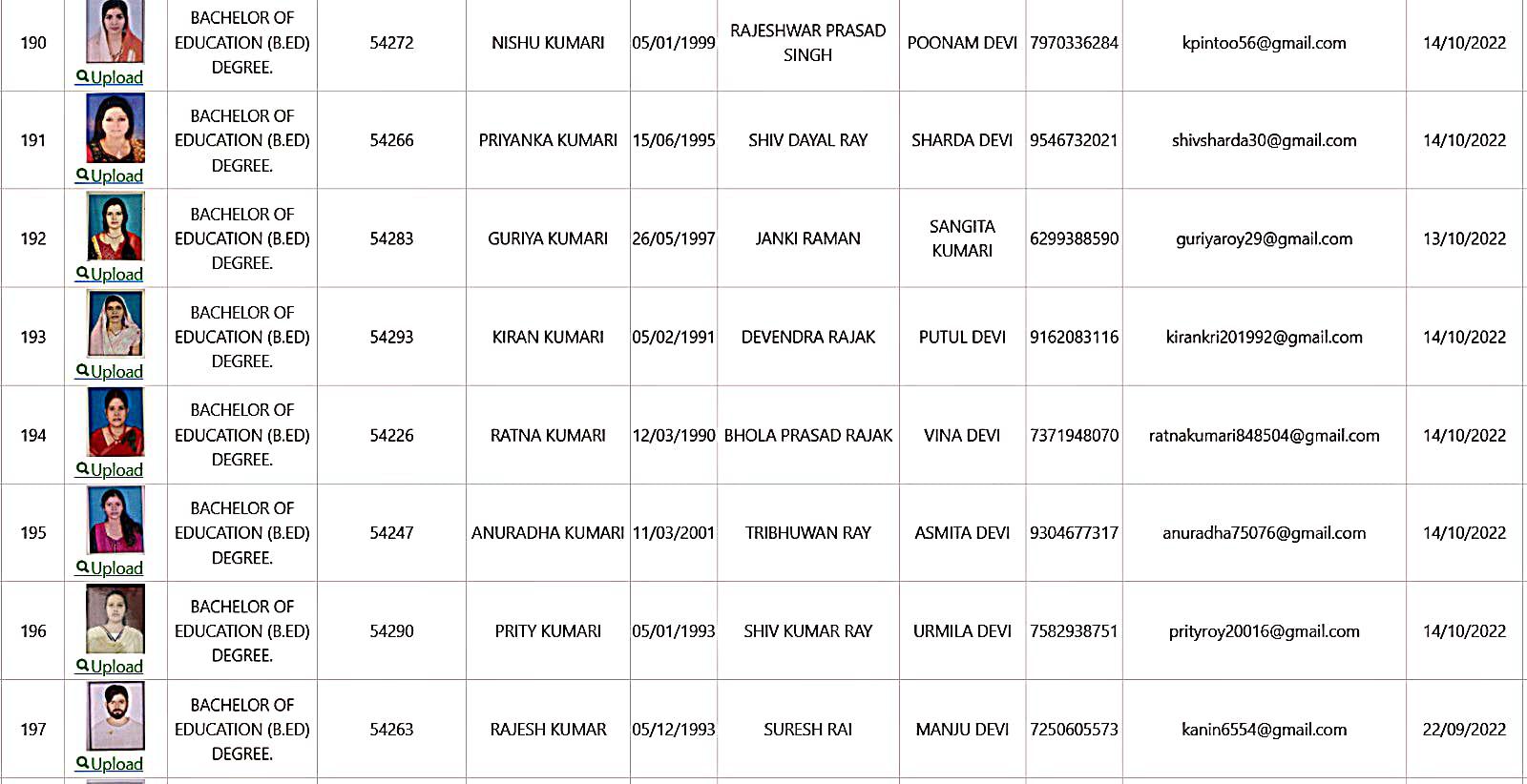
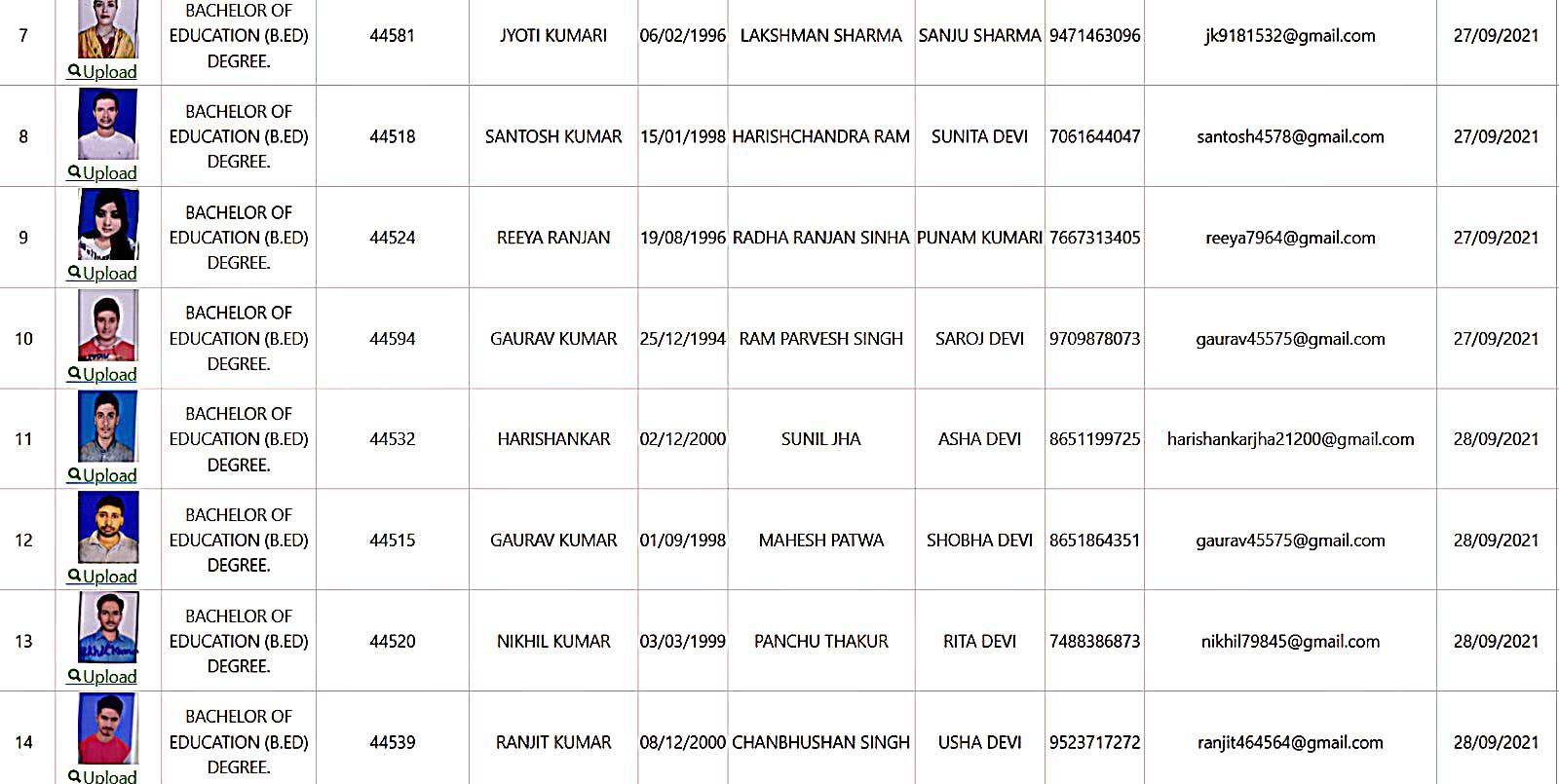
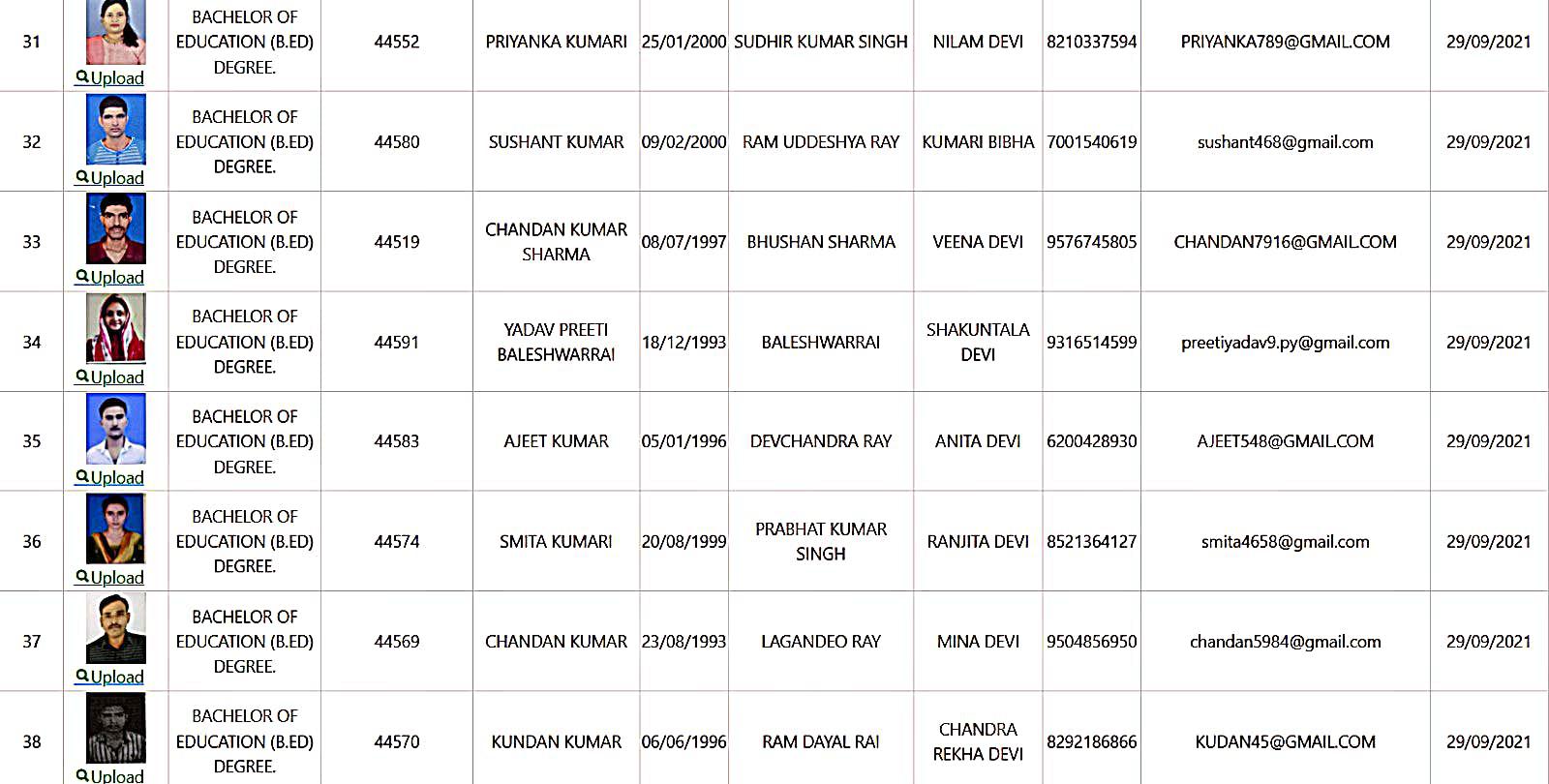
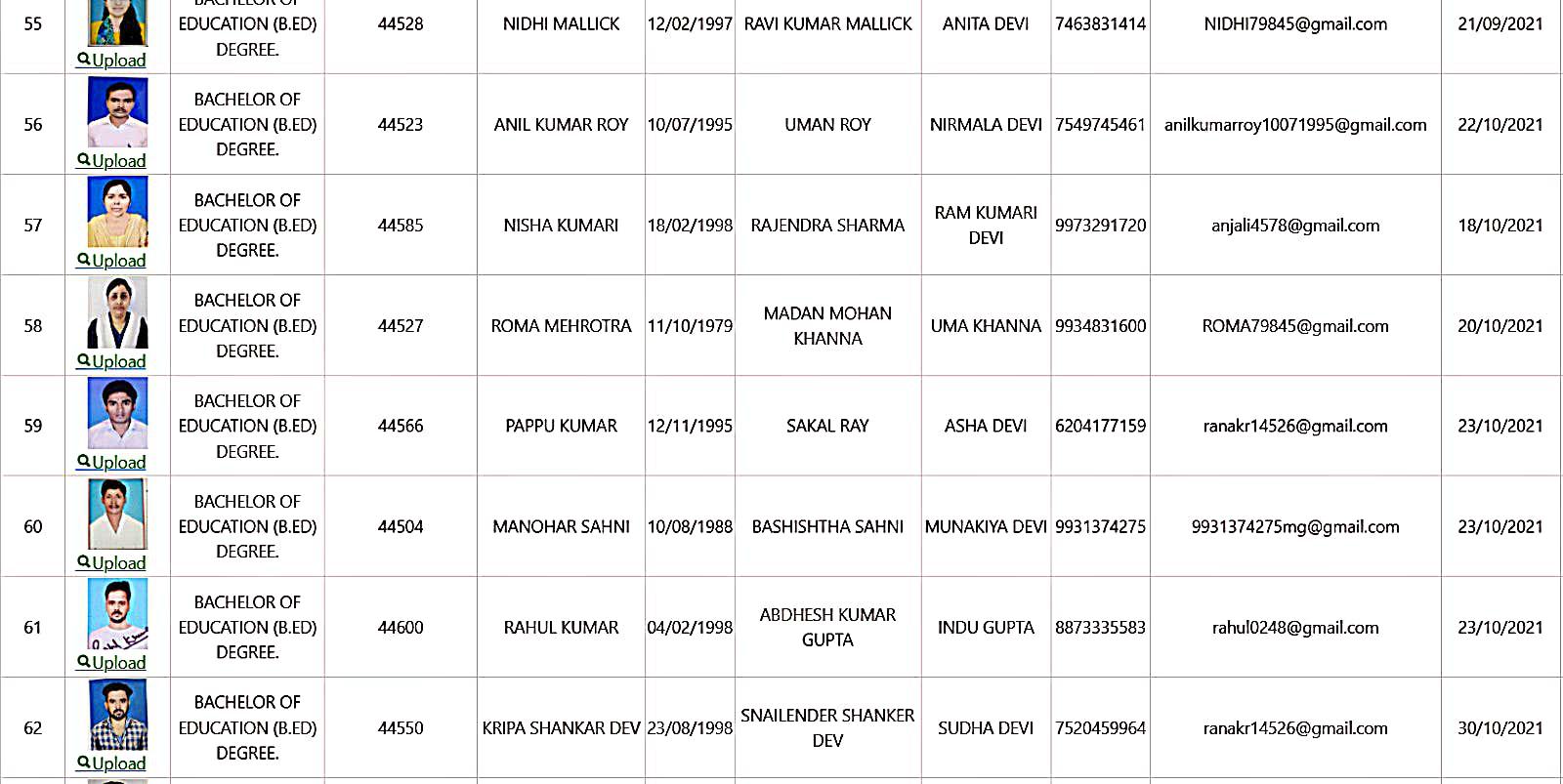
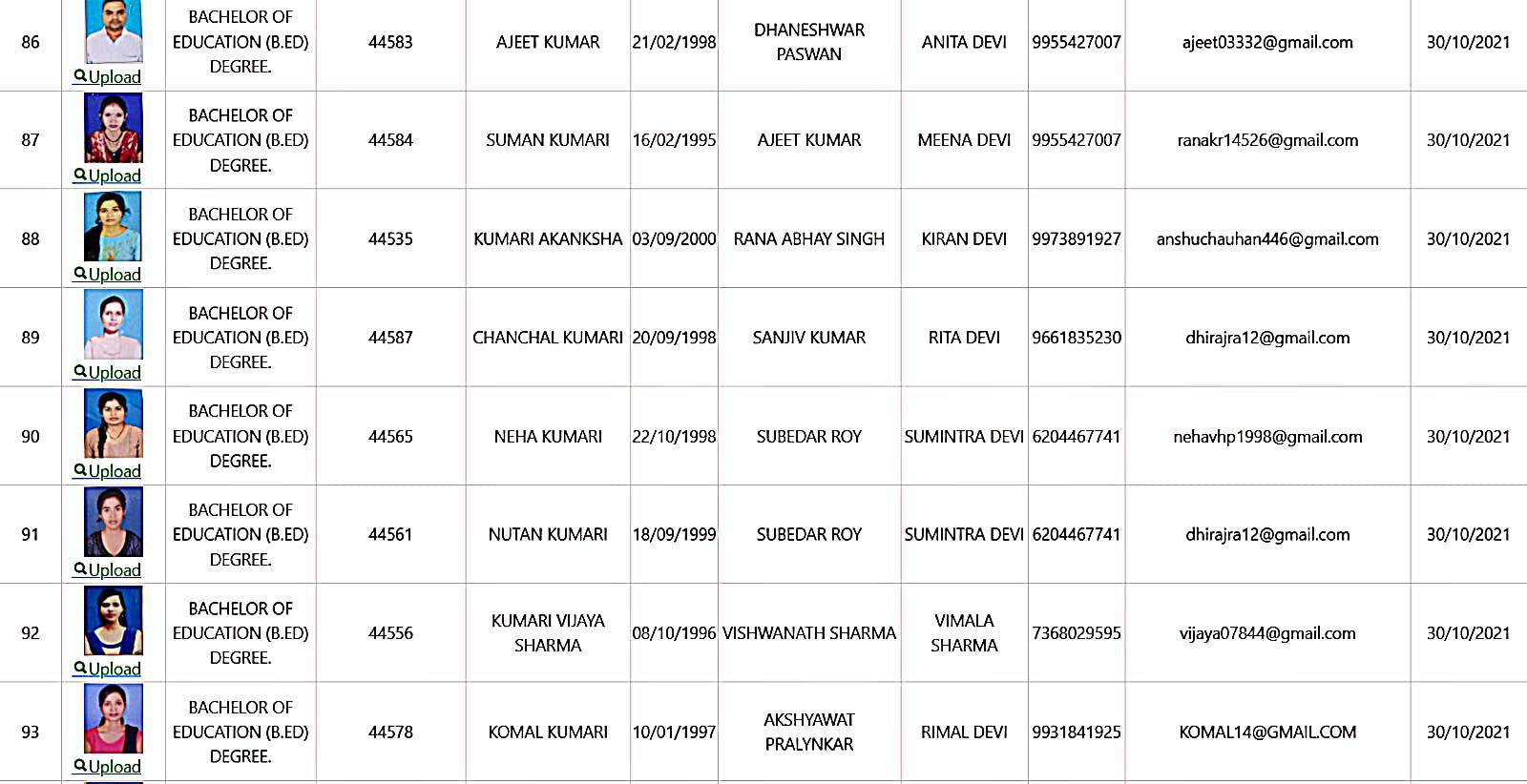
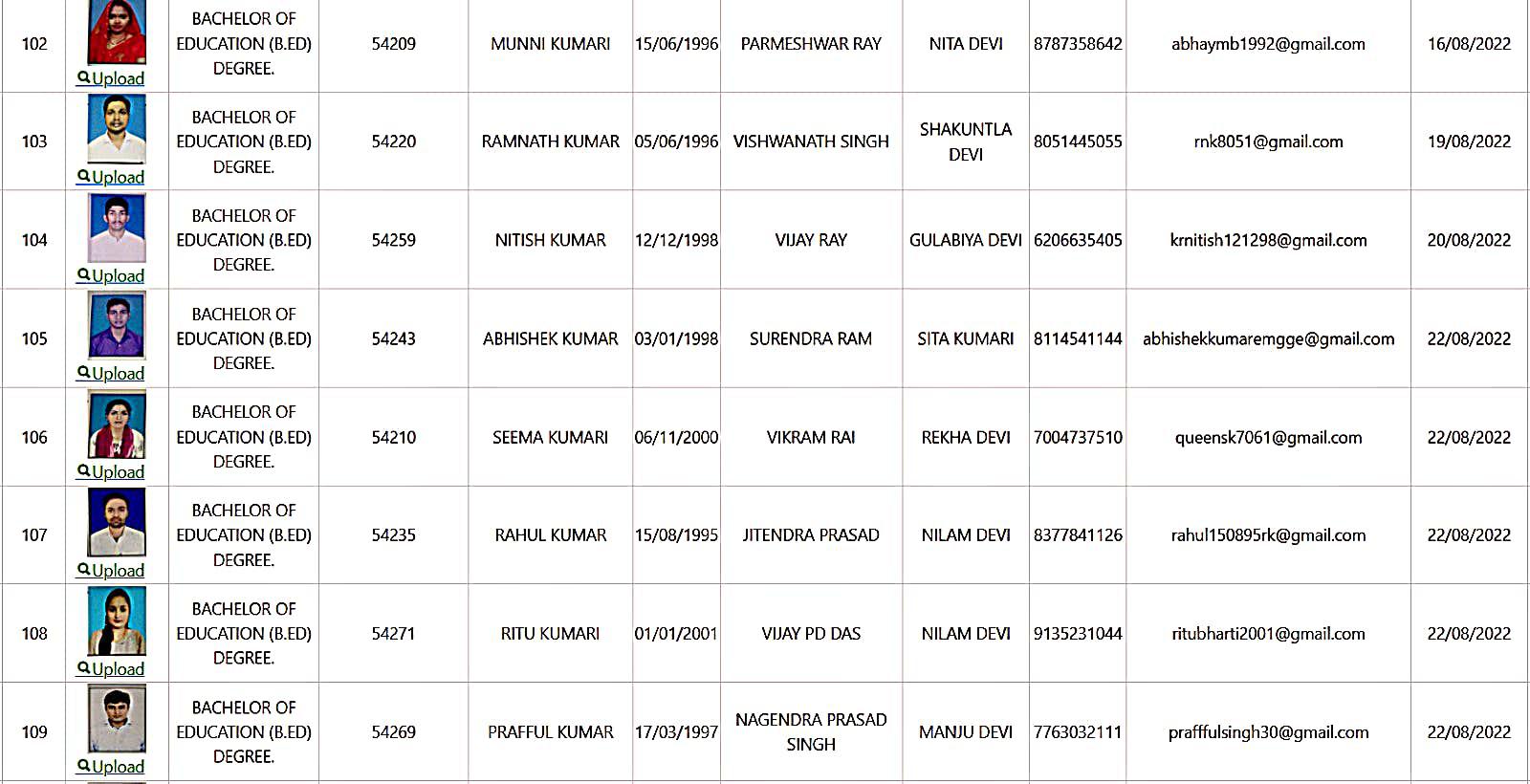
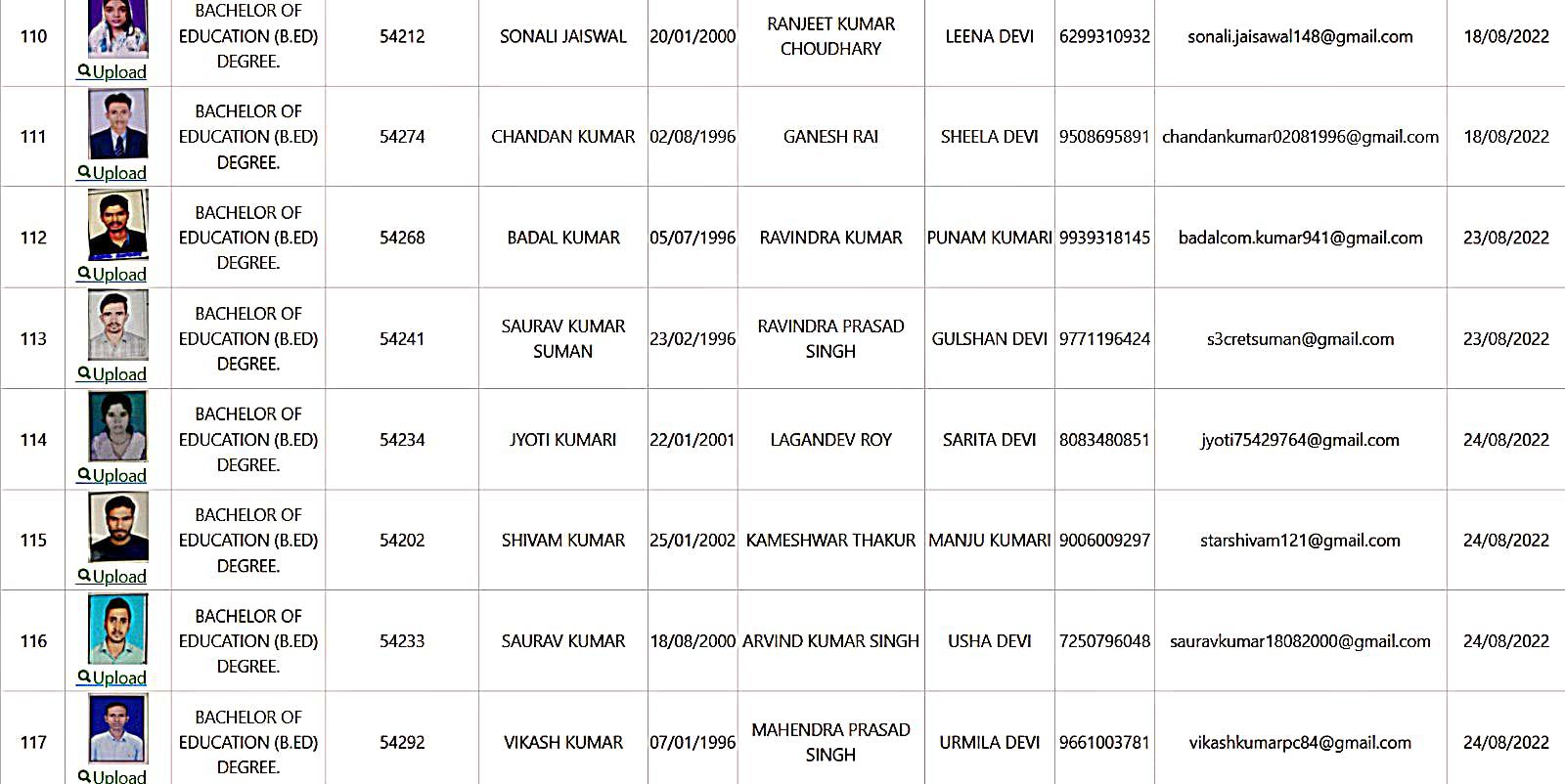
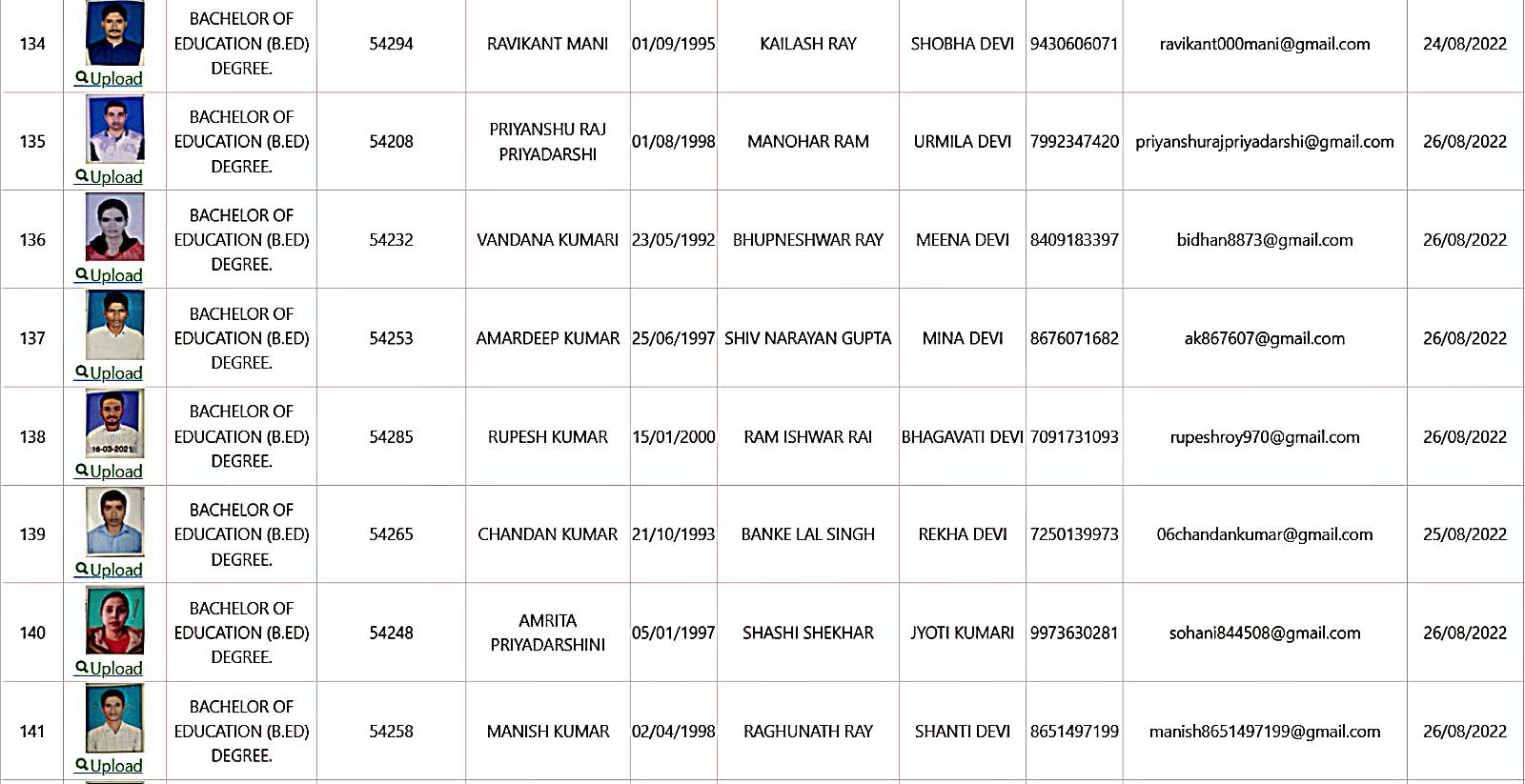
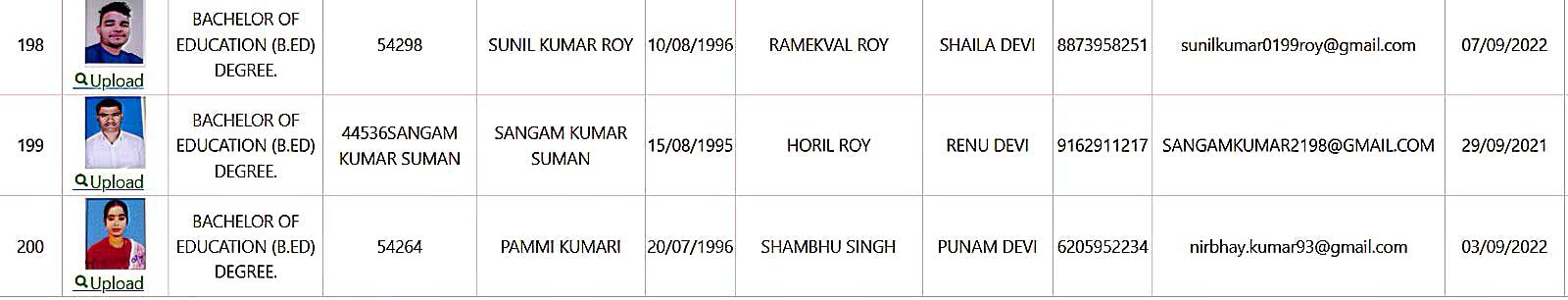
Bachelor of Education Student Details
We at RSRGOI Provide best Education in Bachelor of Education (B.Ed) which is an undergraduate program that prepares individuals for careers in teaching and education. It typically covers various aspects of pedagogy, curriculum development, educational psychology, and classroom management. In many countries, it’s a prerequisite for becoming a certified teacher.
The Bachelor of Education (B.Ed) program is designed to equip students with the knowledge, skills, and competencies required for effective teaching. While the specifics can vary by country and institution, here’s a general overview of what you might expect in a typical B.Ed program:
Curriculum of Bachelor of Education
Educational Psychology: Understanding how students learn and develop, including theories of learning and motivation.
Pedagogy: Methods and strategies for teaching various subjects, including lesson planning, instructional techniques, and classroom management.
Curriculum Development: Designing and evaluating educational materials and activities that align with learning objectives and standards.
Assessment and Evaluation: Techniques for assessing student learning, including tests, quizzes, and formative assessments, as well as how to use assessment data to inform teaching.
Special Education: Understanding the needs of students with disabilities and learning differences, and how to adapt teaching methods accordingly.
Educational Technology: Using technology effectively in the classroom to enhance learning.
Sociology of Education: Examining the role of education in society, including issues of equity, diversity, and inclusion.
Classroom Management: Strategies for creating and maintaining a positive and productive learning environment.
Field Experience/Student Teaching: Practical experience in a classroom setting, often including supervised teaching and observation.
- Duration of Bachelor of Education
Typically, the B.Ed program lasts 3-4 years, depending on the country and the specific requirements of the institution.
Admission Requirements in Bachelor of Education
- Educational Background: Completion of secondary education or equivalent. Some programs may require specific high school subjects.
- Entrance Exams: In some countries, you might need to pass an entrance exam or meet minimum score requirements.
- Application Materials: Often include transcripts, recommendation letters, a personal statement, and sometimes an interview.
Career Prospects
- Teaching: Primary and secondary school teaching in various subjects.
- Educational Administration: Roles such as school principals or educational coordinators.
- Special Education: Working with students with special needs.
- Educational Counseling: Providing guidance and support to students regarding academic and personal issues.
- Curriculum Development: Designing educational materials and programs.
Certification
- In many regions, completing a B.Ed program is a step toward obtaining teaching certification or licensure, which may require additional exams or assessments.
A Bachelor of Education (B.Ed) degree opens up a range of career opportunities in the field of education and beyond. Here are some common and diverse career paths you might consider:
1. Teaching
- Primary/Elementary School Teacher: Teach foundational subjects to young students, focusing on literacy, numeracy, and basic life skills.
- Secondary School Teacher: Specialize in teaching specific subjects like mathematics, science, English, history, etc., to older students.
- Subject Specialist Teacher: Focus on specialized subjects such as art, music, physical education, or foreign languages.
2. Educational Administration
- School Principal: Oversee the overall management and administration of a school, including staff, curriculum, and student affairs.
- Vice Principal/Assistant Principal: Support the principal in school management and take on specific administrative duties.
- Educational Coordinator: Develop and implement educational programs and policies within schools or educational institutions.
3. Special Education
- Special Education Teacher: Work with students who have diverse learning needs or disabilities, providing tailored instruction and support.
- Special Education Consultant: Advise schools or organizations on best practices and strategies for supporting students with special needs.
4. Educational Counseling and Support
- School Counselor: Provide emotional and academic support to students, helping them navigate personal and educational challenges.
- Career Counselor: Assist students in exploring career options and planning their educational and career paths.
5. Curriculum Development and Instructional Design
- Curriculum Developer: Design and create educational materials and programs for schools or educational publishers.
- Instructional Designer: Develop educational content and learning experiences for various platforms, including online courses.
6. Educational Technology
- EdTech Specialist: Integrate technology into the classroom and develop digital learning tools and resources.
- eLearning Designer: Create online learning materials and manage virtual classroom environments.
7. Higher Education and Academia
- Lecturer/Professor: Teach and conduct research at universities or colleges, often requiring advanced degrees beyond a B.Ed.
- Educational Researcher: Conduct research on educational practices, policies, and student outcomes.
8. Nonprofit and Community Education
- Program Coordinator: Develop and manage educational programs for community organizations, nonprofits, or after-school programs.
- Education Advocate: Work on policy development or advocate for educational reforms and improvements at the local, state, or national level.
9. Corporate Training and Development
- Corporate Trainer: Design and deliver training programs for employees in various industries, focusing on skills development and professional growth.
- Organizational Development Specialist: Work on improving organizational practices and employee performance through training and development programs.
10. Educational Publishing
- Educational Publisher: Develop textbooks, learning materials, and other resources for educational institutions and learners.
Additional Considerations
- Continued Education: Many careers in education may benefit from additional qualifications or certifications, such as a Master’s degree or specialized training.
- Entrepreneurship: Some educators choose to start their own educational businesses or consultancy services.
The B.Ed degree provides a solid foundation for a variety of roles within and outside of traditional classroom settings. If you have specific interests or goals, you might tailor your career path accordingly, and further specialization or training can open additional doors.
The Bachelor of Education (B.Ed) is a crucial degree for several reasons, particularly within the field of education. Here’s why the B.Ed is so important:
. Foundation for Teaching Careers
- Professional Preparation: The B.Ed program provides foundational knowledge and practical skills necessary for effective teaching. This includes understanding pedagogical theories, classroom management, curriculum design, and assessment strategies.
- Certification Requirement: In many countries, a B.Ed is a prerequisite for obtaining teaching certification or licensure. It ensures that educators meet the professional standards required to teach in schools.
Development of Teaching Skills
- Pedagogical Expertise: The B.Ed curriculum focuses on how to teach various subjects effectively, tailor instruction to diverse learners, and utilize different teaching methods.
- Classroom Management: Training in managing a classroom effectively, which is crucial for creating a productive learning environment and addressing diverse student needs.
Understanding of Educational Psychology
- Student Development: Knowledge of educational psychology helps teachers understand how students learn and develop, enabling them to better support their cognitive, emotional, and social growth.
- Learning Strategies: Teachers learn strategies to address different learning styles and needs, improving student engagement and achievement.
Curriculum and Instructional Design
- Curriculum Planning: The B.Ed program equips future educators with skills to design and implement curricula that meet educational standards and cater to various learning needs.
- Instructional Design: It provides insights into creating effective instructional materials and assessments that enhance the learning experience.
Specialized Knowledge
- Special Education: Many B.Ed programs include training in special education, preparing educators to work with students who have disabilities or special needs.
- Educational Technology: Training in the integration of technology in the classroom, which is increasingly important in modern education.
Practical Experience
- Student Teaching: The B.Ed often includes a student teaching component, offering hands-on experience in a real classroom setting. This practical experience is invaluable for developing confidence and competence as a teacher.
- Fieldwork: Opportunities for observation and participation in educational settings help bridge theoretical knowledge with practical application.
Career Flexibility and Advancement
- Diverse Opportunities: The B.Ed opens doors to various roles within the education sector, including teaching, administration, curriculum development, and educational counseling.
- Advanced Studies: It provides a strong foundation for further studies in education, such as Master’s or Doctoral programs, which can lead to advanced roles in academia or research.
Impact on Student Outcomes
- Quality Education: Educators with a B.Ed are equipped to deliver high-quality education, which directly impacts student learning outcomes and overall educational effectiveness.
- Student Support: Well-trained teachers can better address the diverse needs of students, helping them achieve their academic and personal potential.
Professionalism and Ethical Standards
- Ethical Teaching: The B.Ed program emphasizes ethical practices in education, ensuring that teachers uphold professional standards and contribute positively to the educational community.
- Continuous Improvement: It encourages ongoing professional development and reflective practice, which are essential for staying current with educational advancements and improving teaching effectiveness.
10. Community and Social Impact
- Community Engagement: Teachers play a critical role in their communities by shaping the next generation, promoting lifelong learning, and addressing societal issues through education.
- Advocacy: Educators can advocate for educational reforms and improvements, contributing to the betterment of the education system and society as a whole.
Overall, the B.Ed is fundamental in shaping competent, skilled, and knowledgeable educators who can make a significant impact in schools and educational settings.